What is artificial
intelligence?
While a number of definitions of artificial
intelligence (AI) have surfaced over the last few decades, John McCarthy offers
the following definition in this 2004 paper (link resides outside ibm.com),
" It is the science and engineering of making intelligent machines,
especially intelligent computer programs. It is related to the similar task of
using computers to understand human intelligence, but AI does not have to
confine itself to methods that are biologically observable." (McCarthy, 2004)
However, decades before this definition, the birth of
the artificial intelligence conversation was denoted by Alan Turing's seminal
work, "Computing Machinery and Intelligence"(link resides outside
ibm.com), which was published in 1950. In this paper, Turing, often referred to
as the "father of computer science", asks the following question,
"Can machines think?" From
there, he offers a test, now famously known as the "Turing Test",
where a human interrogator would try to distinguish between a computer and
human text response. While this test has undergone much scrutiny since its
publish, it remains an important part of the history of AI as well as an
ongoing concept within philosophy as it utilizes ideas around linguistics. (Turing, 1950)
How
does artificial intelligence (AI) work?
“Using
math and logic, a computer system simulates the reasoning that humans use to
learn from new information and make decisions. An artificially intelligent
computer system makes predictions or takes actions based on patterns in
existing data and can then learn from its errors to increase its accuracy.”
Characteristics
1.
Ability to learn
and improve: AI systems can learn from data and improve their performance over
time.
2.
Automation: AI can
automate repetitive tasks and increase efficiency in various industries.
3.
Decision-making:
AI can analyze large amounts of data and make decisions based on that data.
4.
Personalization:
AI can be used to personalize experiences for users, such as in the case of
recommendation systems.
5.
Prediction: AI can
predict outcomes based on historical data and patterns.
Purpose
The applications of artificial intelligence (AI) in
different sectors have become agendas for discussions in the highest circle of
experts. The applications of AI can help society and can harm society even by
jeopardizing human rights. The purpose of this study is to examine the
evolution of AI and its impacts on human rights from social and legal
perspectives.
The
Future
So, what is in store for the future? In the immediate
future, AI language is looking like the next big thing. In fact, it’s already
underway. I can’t remember the last time I called a company and directly spoke
with a human. These days, machines are even calling me! One could imagine
interacting with an expert system in a fluid conversation or having a
conversation in two different languages being translated in real time. We can
also expect to see driverless cars on the road in the next twenty years (and that
is conservative). In the long term, the goal is general intelligence, that is a
machine that surpasses human cognitive abilities in all tasks. This is along
the lines of the sentient robot we are used to seeing in movies. To me, it
seems inconceivable that this would be accomplished in the next 50 years. Even
if the capability is there, the ethical questions would serve as a strong
barrier against fruition. When that time comes (but better even before the time
comes), we will need to have a serious conversation about machine policy and
ethics (ironically both fundamentally human subjects), but for now, we’ll allow
AI to steadily improve and run amok in society.
Everything
about the evolution of artificial intelligence
Artificial Intelligence has grown into a formidable
tool in recent years allowing robots to think and act like humans. Furthermore,
it has attracted the attention of IT firms all around the world and is seen as
the next major technological revolution following the growth of mobile and
cloud platforms. It’s even been dubbed the “4th industrial revolution” by some.
Researchers have developed software that uses Darwinian evolution ideas, such
as “survival of the fittest,” to construct AI algorithms that improve
generation to generation with no need for human intervention. The computer was
able to recreate decades of AI research in only a few days, and its creators
believe that one day it will be able to find new AI techniques. In this
article, we will learn about how AI is evolving day by day.
CHAT
BOT
“A
chatbot is a computer program that simulates human conversation to solve
customer queries. When a customer or a lead reaches out via any channel, the
chatbot is there to welcome them and solve their problems.”
How
Chatbots Work
Chatbots are most used on business websites. When you
have spent a couple of minutes on a website, you can see a chat or voice
messaging prompt pop up on the screen. Those are chatbots. Chatbots had a
humble start as computer programs that used keywords and pattern matching to
respond to users’ questions based on a pre-written script.
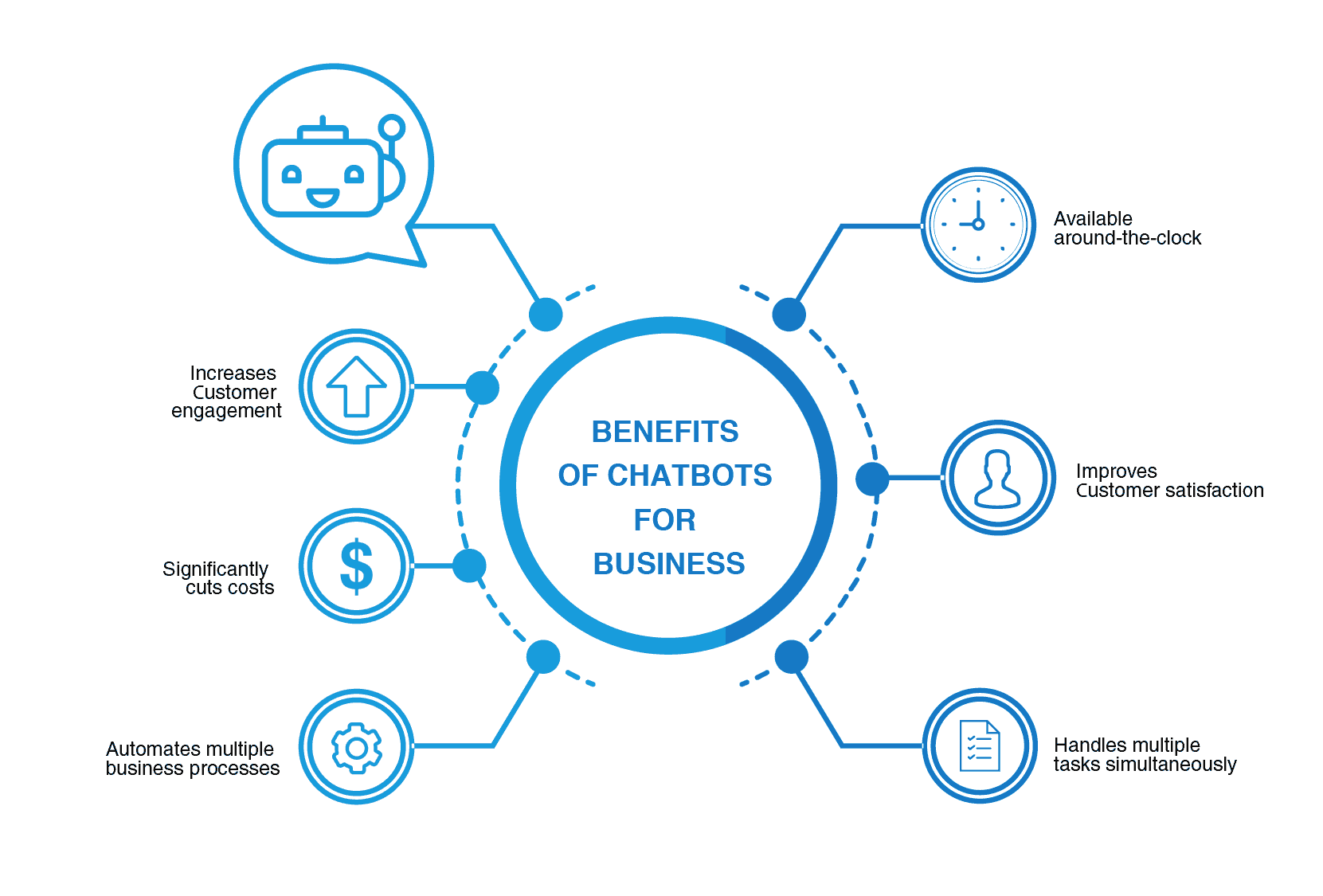
Benefits
of Chatbots
We’ve already discussed that chatbots improve customer
experience. But enhanced customer experience is not the only benefit of using
chatbots. An organization has many advantages of using chatbots for business
growth, process efficiency and cost reduction:
-
Cost-effectiveness:
A chatbot is a one-time investment. Once it has been developed and implemented,
you can scale down on hiring people for customer support. Instead, people can
be engaged in solving complex problems and creating strategies for business growth.
Chatbots also do not make mistakes for established processes, unlike human
agents.
-
Save time:
Chatbots can handle routine repetitive tasks and do them much faster than
humans.
-
Available 24/7:
Chatbots can be available to customers 24/7 without much effort. This can, in
turn, lead to more satisfied customers who wouldn’t hesitate to recommend your
product or services to their network.
-
Reduce customer
wait time: Each chatbot can interact with multiple customers simultaneously,
reducing the size of the wait queue. People can get real-time answers to their
queries when interacting with chatbots.
-
Identify business
leads: You already know that AI chatbots are experts at identifying patterns
and keywords. As chatbots handle the initial support interaction with customers
or prospects, they can be programmed to identify leads by listening to the words
and phrases used by the customers.
What
Is Data Crunching?
“Data
crunching refers to key initial steps required to prepare large volumes of raw
data for analysis. It includes stripping out unwanted information and
formatting, translating data into the required format and structuring it for
analysis or processing by other applications.”
Data
Crunching Explained
Data crunching is needed to convert raw data into a
form suitable for analysis. It commonly involves clearing out proprietary
formatting and unwanted data, converting number and date formats and
reformatting and structuring the information. It can also involve eliminating
duplicated and erroneous data. Data crunching may be needed for a variety of
different reasons. A company may need to convert information from external data
feeds so it can apply its existing business intelligence tools to the data.
Also, if the company’s departments use different applications, it may need to
massage data into a common format so it can report on information from across
the entire business.
Data
Crunching Benefits
Converting raw data into a usable form can be extremely
time-consuming for data scientists, so it makes sense to automate data
crunching as much as possible using programming languages or other tools. An
efficient data crunching process:
-Saves
time: This means companies can save time by focusing their analysis efforts on
the most relevant data. Automating data crunching also accelerates the process
of cleaning up raw data, so companies also have more up-to-date information
available for analysis.
-Saves
money: The time savings translate into lower analysis costs. Highly paid data
scientists and business analysts can use their time more efficiently analyzing
the most valuable information instead of hunting through vast amounts of raw
data.
What
Is Machine Learning (ML)?
“The
basic concept of machine learning in data science involves using statistical
learning and optimization methods that let computers analyze datasets and
identify patterns.”
Since a machine learning algorithm update
autonomously, the analytical accuracy improves with each run as it teaches
itself from the data it analyzes. This iterative nature of learning is both
unique and valuable because it occurs without human intervention — empowering
the algorithm to uncover hidden insights without being specifically programmed
to do so.
The purpose of machine learning is to use machine
learning algorithms to analyze data. By leveraging machine learning, a
developer can improve the efficiency of a task involving large quantities of
data without the need for manual human input. Around the world, strong machine
learning algorithms can be used to improve the productivity of professionals
working in data science, computer science, and many other fields.
Evolution
of Machine Learning
According
to Forbes, the origins of machine learning date back to 1950. Speculating on
how one could tell if they had developed a truly integrated artificial
intelligence (AI), Alan Turing created what is now referred to as the Turing
test, which suggests that one way of testing whether or not the AI is capable
of understanding language is to see if it’s able to fool a human into thinking
they are speaking to another person.
What
Are Artificial Neural Networks
“An
artificial neural network is an attempt to simulate the network of neurons that
make up a human brain so that the computer will be able to learn things and
make decisions in a humanlike manner.”
How
do artificial neural networks work?
Artificial neural networks use different layers of
mathematical processing to make sense of the information it’s fed. Typically,
an artificial neural network has anywhere from dozens to millions of artificial
neurons—called units—arranged in a series of layers. The input layer receives
various forms of information from the outside world. This is the data that the
network aims to process or learn about. From the input unit, the data goes
through one or more hidden units.
What
are artificial neural networks used for?
“As the networks process and learn from data they can
classify a given data set into a predefined class, it can be trained to predict
outputs that are expected from a given input and can identify a special feature
of data”
What
is the Turing Test?
“The
Turing Test involves three players: a computer, a human respondent, and a human
interrogator. All three are placed in separate rooms or in the same room but
physically separated by terminals.”
The interrogator asks both players a series of
questions and, after a period, tries to determine which player is the human and
which is the computer. If the interrogator fails to determine which player is
which, the computer is declared the winner, and the machine is described as
able to think.
“The game involves a human guessing if a player is a
computer or another human.”
The
challenges of artificial intelligence by using real life examples
As
such, there exists much as-yet-untapped potential, with growing career
prospects. Many top employers seek professionals with the skills, expertise,
and knowledge to propel their organizational aims forward. Career pathways may
include:
1. Robotics and self-driving/autonomous cars (such as
Waymo, Nissan, Renault)
2. Healthcare (for instance, multiple applications in
genetic sequencing research, treating tumors, and developing tools to speed up
diagnoses including Alzheimer’s disease)
3. Academia (leading universities in AI research include
MIT, Stanford, Harvard, and Cambridge)
4. Retail (Amazon shops and other innovative shopping
options)
5. Banking
What are the risks of artificial intelligence?
“The use of artificial intelligence systems in
decision-making processes carries certain risks due to the potential direct or
indirect impacts of the implementation of these technologies. Some of these
risks include:’’ (Pombo, 2022)
The leakage of personal data that can compromise
people's well-being.
Extreme surveillance and subsequent manipulation by
private or government organizations with access to the information that feeds
artificial intelligence technologies.”
The "echo chambers" or "filter bubbles" that occur when you are exposed to the same ideas, news and/or facts, which is a common phenomenon among social media users and ends up strengthening preconceived biases. This is especially dangerous among decision-makers in any area, but even more so among those working on public policy. (Pombo, 2022)
“Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence”
Limits of adaptation: Unlike what happens with human
beings, machines that work with Artificial Intelligence lack the adaptive
capacity of humans. For example, in crisis situations or changing environments,
machines have very limited ability to adapt and solve problems. However, this
is a problem that, probably in the future, can be solved thanks to Machine
Learning. Although, for now, it is still a major disadvantage when it comes to
talking about Artificial Intelligence. (https://www.beetrack.com/es/blog/ventajas-y-desventajas-de-la-inteligencia-artificial,
2023)
It encourages unemployment: Although the use of
Artificial Intelligence can encourage humans to focus on more complex and
responsible tasks, in many cases, its use can lead to unemployment. This is
especially a problem in the case of lower-skilled jobs, where intelligent
machines are far more efficient at carrying them out than any human worker.
(https://www.beetrack.com/es/blog/ventajas-y-desventajas-de-la-inteligencia-artificial,
2023)
Ethical Challenges
1. The lack of transparency of AI tools: AI decisions are not always intelligible to humans.
2. AI is not neutral: AI-based decisions are susceptible to inaccuracies, discriminatory outcomes, embedded or embedded biases.
3. Surveillance practices for data collection and the privacy of court users. (unesco, 2023)
Weak Artificial Intelligence: What It Is and How It
Has Impacted Society
Universities of the Pacific Rim (APRU) with the
support of Google, the professor of the Faculty of Physical and Mathematical
Sciences (FCFM) and researcher at the Center for Mathematical Modeling, Felipe
Tobar, is developing a work on weak Artificial Intelligence and what its social
consequences are. The academic explores the daily use of devices classified as
"intelligent machines", and the concerns generated by the lack of
knowledge that exists regarding their limits. (Ramires, 2020)
Artificial Intelligence and Authorship
A tweet has recently circulated giving instructions on how to remove a peanut butter sandwich from a video recorder, written in the style of a Bible verse. It's a lot of fun, at least until you realize it was written by an AI bot. At that stage he becomes very intelligent but loses all humor. It seems that ingenuity lies in the clever use of language; the self-conscious parody of a shared understanding of the form being imitated. Once it has been revealed that the author is a computer program, all of this is lost; It's simply a tool that applies rules you've learned. (levene, 2023)
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Artificial
Intelligence Systems in Intelligence Analysis
He U.S. military and intelligence community have shown
interest in developing and deploying artificial intelligence (AI) systems to
support intelligence analysis, both as an opportunity to leverage new
technology and as a solution for an ever-proliferating data glut. However,
deploying AI systems in a national security context requires the ability to
measure how well those systems will perform in the context of their mission.
(Daniel Ish, 2021)
To address this issue, the authors begin by
introducing a taxonomy of the roles that AI systems can play in supporting
intelligence—namely, automated analysis, collection support, evaluation
support, and information prioritization—and provide qualitative analyses of the
drivers of the impact of system performance for each of these categories.
(Daniel Ish, 2021)
The authors then single out information prioritization
systems, which direct intelligence analysts' attention to useful information
and allow them to pass over information that is not useful to them, for
quantitative analysis. Developing a simple mathematical model that captures the
consequences of errors on the part of such systems, the authors show that their
efficacy depends not just on the properties of the system but also on how the
system is used. Through this exercise, the authors show how both the calculated
impact of an AI system and the metrics used to predict it can be used to
characterize the system's performance in a way that can help decisionmakers
understand its actual value to the intelligence mission. (Daniel Ish, 2021)
Key Findings
- Using
metrics not matched to actual priorities obscures system performance and
impedes informed choice of the optimal system.
- Metric choice should take place before the system is built and be guided by attempts to estimate the real impact of system deployment.
- Effectiveness, and therefore the metrics that measure it, can depend not
just on system properties but also on how the system is used.
- A key consideration for decisionmakers is the number of resources devoted to the mission outside those devoted to building the system. (Daniel Ish, 2021)
Recommendations
1. Begin with the right metrics. This requires having a detailed understanding of the way an AI system will be used and choosing metrics that reflect success with respect to this utilization.
2. Reevaluate (and retune) regularly. Because the world around the system continues to evolve after deployment, system evaluation must continue as a portion of regular maintenance.
3. Speak the language. System designers have a well-established set of metrics for capturing the performance of AI systems, and being conversant in these traditional metrics will ease communication with experts during the process of designing a new system or maintaining an existing one.
4. Conduct further research into methods of evaluating AI system
effectiveness. (Shacklett, 2019)
The true costs and ROI of implementing AI in the
enterprise in 2019, web content evaluator Market Muse revealed that 80% of IT
and corporate business leaders wanted to learn more about the cost of
implementing existing artificial intelligence (AI) technology; 74% were
interested in how much more it would cost over present expenditure levels to
implement AI in their enterprises; and 69% wanted more information about how to
measure the return on investment (ROI) for a new AI solution. (Shacklett,
2019)
Bibliografía
Anyoha, R. (2017). Special
Edition on Artificial Intelligence.
https://sitn.hms.harvard.edu/flash/2017/history-artificial-intelligence/.
Berkely, U. (26 de
Junio de 2020). University of California, Berkeley. Obtenido de University of California, Berkeley:
https://ischoolonline.berkeley.edu/blog/what-is-machine-learning/
Brooks, R. (21 de March de
2022). University of York . Obtenido de University of York :
https://online.york.ac.uk/artificial-intelligence-and-its-impact-on-everyday-life/
Chatterjee, S. S. (2021). Evolution
of artificial intelligence and its impact on human rights: from sociolegal
perspective. . International Journal of Law and Management, 64(2),
184-205.
Chowdhury, M. (2021). The
Evolution of Artificial Intelligence: Past, Present & Future.
https://www.analyticsinsight.net/the-evolution-of-artificial-intelligence-past-present-future/.
Kekatos, M. (21 de July
de 2023). ABCNews. Obtenido de ABCNews:
https://abcnews.go.com/US/turing-test-determines-computers/story?id=101486628
Marr, B. (19 de
February de 2016). A Short History of Machine Learning . Obtenido de A Short History of Machine Learning :
https://www.forbes.com/sites/bernardmarr/2016/02/19/a-short-history-of-machine-learning-every-manager-should-read/?sh
Marr, B. (24 de
Septiembre de 2018). Forbes . Obtenido de Forbes :
https://www.forbes.com/sites/bernardmarr/2018/09/24/what-are-artificial-neural-networks-a-simple-explanation-for-absolutely-anyone/
McCarthy, J. (2004). Artificial
Intelligence . https://www.ibm.com/topics/artificial-intelligence.
Microsoft. (2006). Work
of AI.
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/resources/cloud-computing-dictionary/what-is-artificial-intelligence#self-driving-cars.
Morris, A. (2021). What
Is Data Crunching & Why Is It Important?
https://www.netsuite.com/portal/resource/articles/erp/data-crunching.shtml.
Turing, A. (1950). Artificial
Intelligence . https://www.ibm.com/topics/artificial-intelligence.
Watts, R. (2022). What Is
A Chatbot? Everything You Need To Know.
https://www.forbes.com/advisor/business/software/what-is-a-chatbot/.
A.Pilar, S. (21 de mayo de 2023). https://www.rtve.es/noticias/20230527/como-inteligencia-artificial-chatgpt-estan-cambiando-ambito-educativo/2447088.shtml. Obtenido de https://www.rtve.es/noticias/20230527/como-inteligencia-artificial-chatgpt-estan-cambiando-ambito-educativo/2447088.shtml: https://www.rtve.es/noticias/20230527/como-inteligencia-artificial-chatgpt-estan-cambiando-ambito-educativo/2447088.shtml
B.S, C. (16 de Octubre de 2016). https://www.ibm.com/mx-es/ai-cybersecurity.
Obtenido de https://www.ibm.com/mx-es/ai-cybersecurity:
https://www.ibm.com/mx-es/ai-cybersecurity
Barreiro, N. (27 de Abril de 2023). https://anelis.com/10-casos-de-exito-de-empresas-que-han-implementado-inteligencia-artificial/.
Obtenido de
https://anelis.com/10-casos-de-exito-de-empresas-que-han-implementado-inteligencia-artificial/:
https://anelis.com/10-casos-de-exito-de-empresas-que-han-implementado-inteligencia-artificial/
Barrera, T. (3 de Diciembre de 2021). https://thetechfashionista.com/es/inteligencia-articifial-en-la-industria-de-la-moda/.
Obtenido de
https://thetechfashionista.com/es/inteligencia-articifial-en-la-industria-de-la-moda/:
https://thetechfashionista.com/es/inteligencia-articifial-en-la-industria-de-la-moda/
Daniel Ish, J. E. (2021). https://www.rand.org/pubs/research_reports/RRA464-1.html.
Obtenido de https://www.rand.org/pubs/research_reports/RRA464-1.html:
https://www.rand.org/pubs/research_reports/RRA464-1.html
Dilmegani, C. (9 de Octubre de 2023). https://research.aimultiple.com/ai-usecases/.
Obtenido de https://research.aimultiple.com/ai-usecases/:
https://research.aimultiple.com/ai-usecases/
https://www.beetrack.com/es/blog/ventajas-y-desventajas-de-la-inteligencia-artificial. (8 de 5 de 2023). Obtenido de
https://www.beetrack.com/es/blog/ventajas-y-desventajas-de-la-inteligencia-artificial:
https://www.beetrack.com/es/blog/ventajas-y-desventajas-de-la-inteligencia-artificial
levene, A. (23 de febrero de 2023). https://publicationethics.org/news/artificial-intelligence-and-authorship.
Obtenido de
https://publicationethics.org/news/artificial-intelligence-and-authorship:
https://publicationethics.org/news/artificial-intelligence-and-authorship
Pombo, c. (7 de 12 de 2022). https://blogs.iadb.org/conocimiento-abierto/es/riesgos-inteligencia-artificial/.
Obtenido de
https://blogs.iadb.org/conocimiento-abierto/es/riesgos-inteligencia-artificial/:
https://blogs.iadb.org/conocimiento-abierto/es/riesgos-inteligencia-artificial/
RAGHUNANDAN, M. (25 de Septiembre de
2018). https://www.kolabtree.com/blog/es/5-ejemplos-del-mundo-real-de-la-ai-en-la-sanidad/.
Obtenido de
https://www.kolabtree.com/blog/es/5-ejemplos-del-mundo-real-de-la-ai-en-la-sanidad/:
https://www.kolabtree.com/blog/es/5-ejemplos-del-mundo-real-de-la-ai-en-la-sanidad/
Ramires, F. (16 de junio de 2020). https://uchile.cl/noticias/164364/inteligencia-artificial-debil-que-es-y-como-ha-impactado.
Obtenido de
https://uchile.cl/noticias/164364/inteligencia-artificial-debil-que-es-y-como-ha-impactado:
https://uchile.cl/noticias/164364/inteligencia-artificial-debil-que-es-y-como-ha-impactado
Ruiz, A. C. (22 de junio de 2021). https://www.universidadviu.com/es/actualidad/nuestros-expertos/inteligencia-artificial-ventajas-y-desventajas.
Obtenido de https://www.universidadviu.com/es/actualidad/nuestros-expertos/inteligencia-artificial-ventajas-y-desventajas:
https://www.universidadviu.com/es/actualidad/nuestros-expertos/inteligencia-artificial-ventajas-y-desventajas
Samuel.s.Pilar. (27 de mayo de 2023). https://www.rtve.es/noticias/20230527/como-inteligencia-artificial-chatgpt-estan-cambiando-ambito-educativo/2447088.shtml.
Obtenido de
https://www.rtve.es/noticias/20230527/https://www.rtve.es/noticias/20230527/como-inteligencia-artificial-chatgpt-estan-cambiando-ambito-educativo/2447088.shtmlcomo-inteligencia-artificial-chatgpt-estan-cambiando-ambito-educativo/2447088.shtml:
https://www.rtve.es/noticias/20230527/como-inteligencia-artificial-chatgpt-estan-cambiando-ambito-educativo/2447088.shtml
Shacklett, M. (1 de Abril de 2019). https://www.zdnet.com/article/the-true-costs-and-roi-of-implementing-ai-in-the-enterprise/.
Obtenido de
https://www.zdnet.com/article/the-true-costs-and-roi-of-implementing-ai-in-the-enterprise/:
https://www.zdnet.com/article/the-true-costs-and-roi-of-implementing-ai-in-the-enterprise/
unesco. (24 de ABRIL de 2023). https://www.unesco.org/es/artificial-intelligence/recommendation-ethics/cases.
Obtenido de
https://www.unesco.org/es/artificial-intelligence/recommendation-ethics/cases:
https://www.unesco.org/es/artificial-intelligence/recommendation-ethics/cases
world, t. l. (27 de febrero de 2023). https://thelogisticsworld.com/manufactura/como-la-inteligencia-artificial-nos-lleva-a-un-nuevo-capitulo-en-la-manufactura-industrial/#:~:text=Los%20avances%20en%20tecnolog%C3%ADa%20han%20permitido%20a%20los,vanguardia%20en%20el%20campo%20de%20la%20manufac.
Obtenido de
https://thelogisticsworld.com/manufactura/como-la-inteligencia-artificial-nos-lleva-a-un-nuevo-capitulo-en-la-manufactura-industrial/#:~:text=Los%20avances%20en%20tecnolog%C3%ADa%20han%20permitido%20a%20los,vanguardia%20en%20el%20campo%20de%20la%20manufac:
https://thelogisticsworld.com/manufactura/como-la-inteligencia-artificial-nos-lleva-a-un-nuevo-capitulo-en-la-manufactura-industrial/#:~:text=Los%20avances%20en%20tecnolog%C3%ADa%20han%20permitido%20a%20los,vanguardia%20en%20el%20campo%20de%20la%20manufac
.webp)




No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario